1) Introduction
In CNC machining using UMC instead of “5-axis CNC machine” terminology can sometimes lead to confusion. One such instance is the distinction between the Universal Machining Center (UMC) and 5-axis CNC machines. While many might assume they represent different technologies, in reality, they refer to the same advanced machining system. The term “Universal” in UMC emphasizes the machine’s versatility and all-encompassing capabilities. It’s a nod to its ability to perform diverse operations without the need for multiple setups or machines.
On the other hand, the “5-axis” is a more technical descriptor, highlighting the machine’s five degrees of movement. Both terms, UMC and 5-axis CNC, nail the machine’s prowess, but from different perspectives. Whether you come across a Universal Machining Center or a 5-axis CNC machine, know that beneath the terminology lies the same cutting-edge technology, ready to revolutionize manufacturing processes.
5-axis CNC machining is a significant leap from the traditional 3-axis systems. These machines, unlike their predecessors, don’t just operate in the X, Y, and Z linear axes. They introduce two additional rotational axes, often called A and B or C. These rotational axes grant the machine its unique ability to tilt and pivot, ensuring intricate cuts from diverse angles.
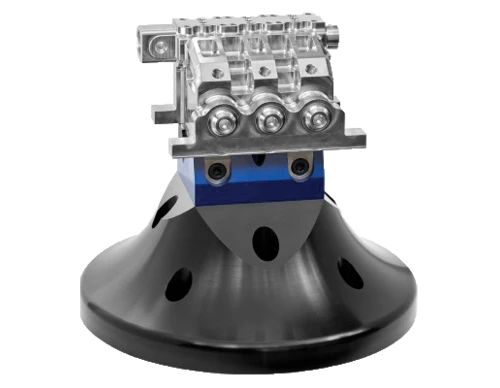
The essence of 5-axis CNC machines is captured in simultaneous machining. This capability allows the machine to maneuver all five axes concurrently, paving the way for crafting complex shapes and undercuts. Such precision is particularly invaluable for sectors like aerospace, where the complexity of components demands such advanced machining.
But what truly sets 5-axis CNC machining apart are the benefits it brings to the table. The need for repositioning is drastically reduced, thanks to the machine’s ability to access multiple angles of a workpiece. This not only trims down production times but also ensures a superior surface finish, minimizing post-processing efforts. In the grand manufacturing scheme, 5-axis CNC machines are not just tools; they are game-changers, promising efficiency and unmatched product quality.
Also, I had previously written an article about well-known Machining Centers which you can check here.
You can check this article for comprehensive information about VMC(vertical machining centers).
Please check this article for more about the HMC(Horizontal machining center).
2) Structure of a Universal Machining Center (UMC)
A Universal Machining Center (UMC) is designed to offer flexibility and precision in machining. Here’s a breakdown of its primary structural components:
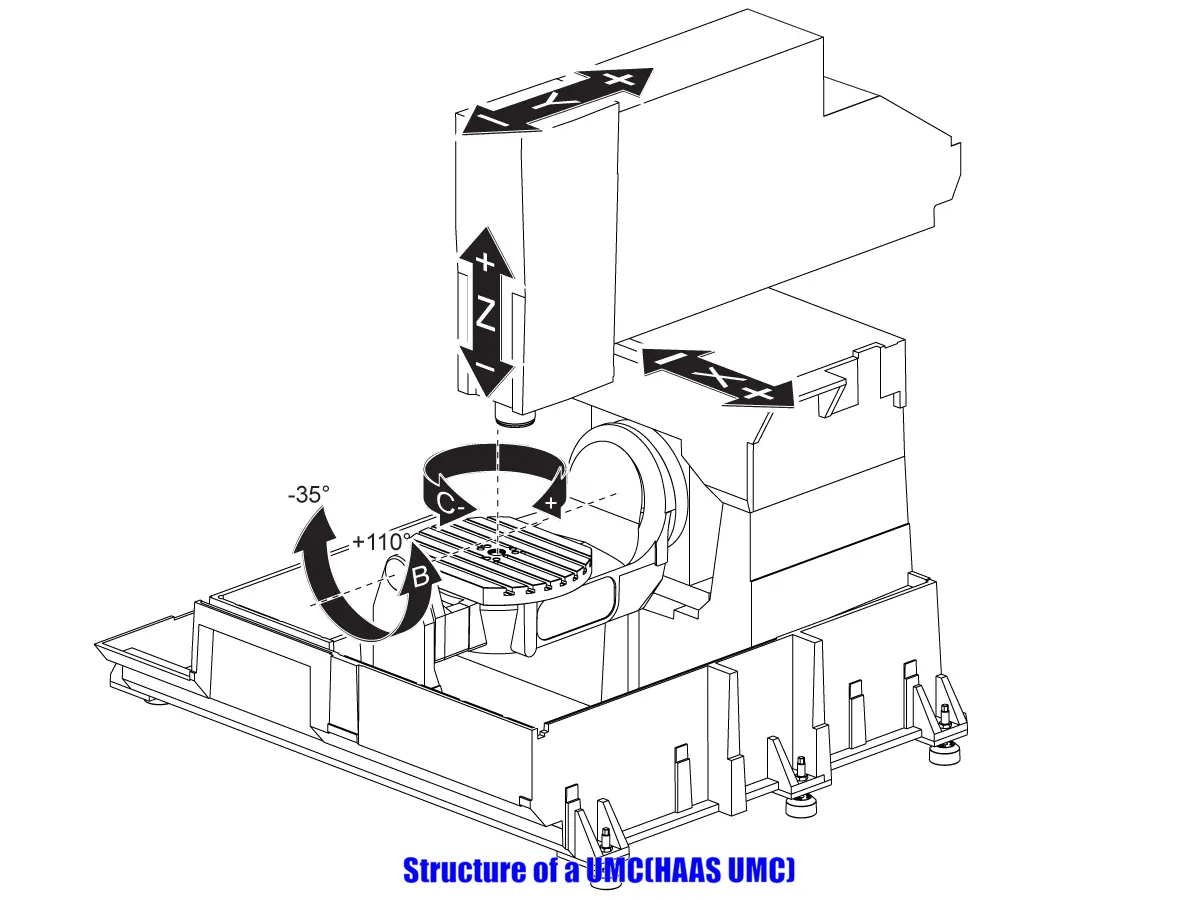
- Spindle: At the heart of the UMC is the spindle, which holds the cutting tool. In a UMC, the spindle can move and rotate in multiple directions, allowing for versatile machining operations.
- Rotational Axes: Unlike traditional 3-axis machines, a UMC boasts two additional rotational axes (A and B or C) that allow the tool or workpiece to tilt and rotate. This capability ensures intricate cuts from diverse angles.
- Table: The table is where the workpiece is mounted. In a UMC, the table can rotate, allowing for multi-sided machining without the need to reposition the workpiece.
- Tool Magazine: This component stores various tools that the machine might need during its operations. The UMC can automatically switch between tools, ensuring seamless transitions between different machining processes.
- Pallet Changer: Some UMCs come equipped with a pallet changer, which allows for the automatic swapping of workpieces. This feature ensures continuous machining, enhancing productivity.
- Control Panel: The brain of the UMC, the control panel, is where operators input commands and oversee the machining process. Modern UMCs come with advanced software interfaces that offer real-time monitoring and feedback.
- Coolant System: To prevent overheating and ensure smooth operations, UMCs are equipped with a coolant system. This system circulates a coolant fluid, reducing heat generated during machining.
- Chip Conveyor: Given the precision and speed of operations, chip management is crucial. The chip conveyor efficiently removes and collects chips produced during the machining process.
- Sturdy Frame: The frame of a UMC is robust and rigid, designed to absorb vibrations and ensure stability during operations. This rigidity is crucial for maintaining precision and achieving high-quality machining results.
3) Applications of 5-Axis CNC Machining
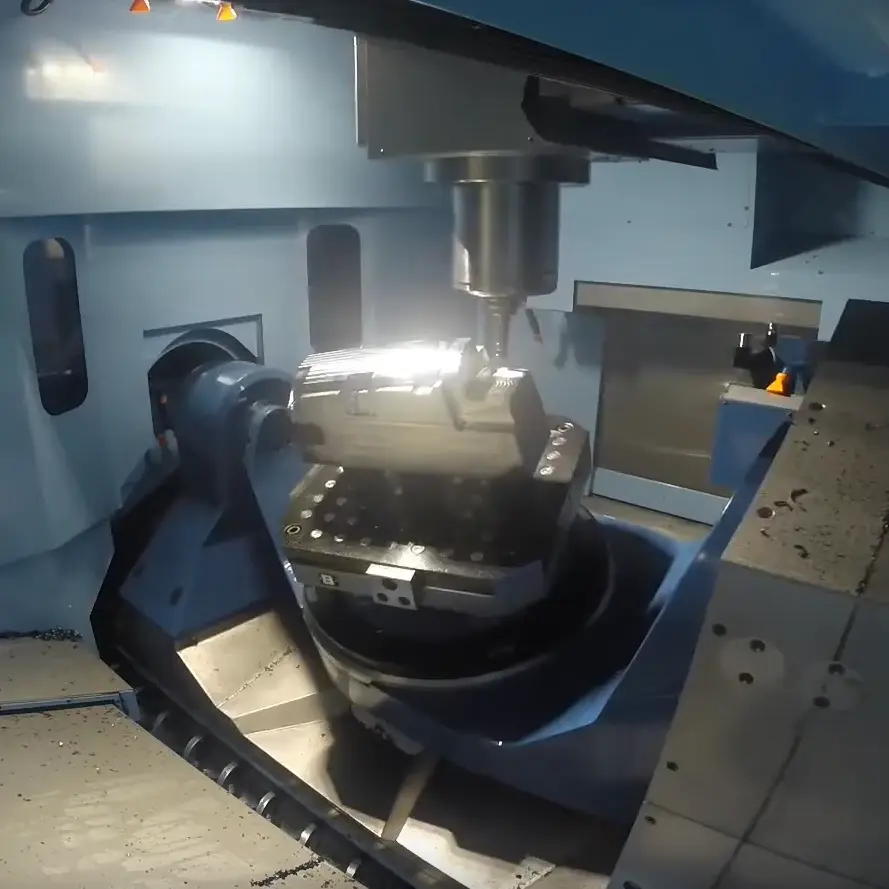

- Aerospace Machining:
- 5-axis CNC machines are indispensable in the aerospace industry due to the intricate geometries and high-tolerance demands of aerospace components.
- They are used for crafting turbine blades, fuselage parts, and engine components.
- The simultaneous movement of five axes ensures parts are machined to the highest standards of accuracy.
- Medical Device Manufacturing:
- The medical industry has greatly benefited from 5-axis CNC machining.
- These machines are used for crafting intricate orthopedic implants and detailed surgical instruments.
- They ensure medical devices are functional and safe for patient use.
- Automotive Industry:
- The automotive industry values the speed and efficiency of 5-axis CNC machines.
- They aid in producing complex engine components, gearboxes, and other critical parts.
- Their ability to produce parts rapidly with minimal setups reduces manufacturing times.
- Complex Part Production:
- For parts that don’t fit into a specific sector, 5-axis CNC machining is the solution.
- It’s used for creating intricate sculptures, unique molds, or one-of-a-kind prototypes.
- The machine’s capabilities ensure complex designs are realized with precision and finesse.
4) Advantages of 5-Axis UMC CNC Machining Center
Universal Machining Centers (5-axis machining centers) have some important points that bold their effectiveness in the area. Below you can check them;
a) Increased Precision: One of the most lauded attributes of 5-axis CNC machines is their unparalleled precision. By maneuvering on five different axes simultaneously, these machines can access intricate parts of a workpiece that would be otherwise challenging. This ensures that every cut, drill, or mill is executed with the utmost accuracy, reducing the margin of error to a negligible minimum.
b) Reduced Setup Time: Time is of the essence in the machining world. With 5-Axis UMC CNC machines, operators can significantly cut down on the setup time. Given their multi-axis configuration, there’s seldom a need to reposition the workpiece multiple times. This speeds up the production process and also reduces the chances of human-induced errors during setups.
c) Complex Geometry Machining: The world of design and manufacturing is no longer confined to simple shapes. As part designs get more complex a need for more capable CNC machines becomes a must. 5-axis CNC machines rise to the occasion, effortlessly machining parts with complicated geometries that would be nearly impossible for 3-axis or 4-axis machines.
d) Improved Surface Finish: Last but certainly not least, 5-axis CNC machines promise an impeccable surface finish. Their ability to maintain the optimal cutting angle ensures that the tool works efficiently, resulting in smoother surfaces. This enhances the appearance of the part and saves the long G-Code post-processing time.
5) Well-known UMC manufacturers
6) Conclusion
In conclusion, UMC CNC machining stands as a pivotal lead, guiding the industry toward precision, efficiency, and innovation. The introduction of Universal Machining Centers (UMC) and the prowess of 5-axis CNC machines have revolutionized the way we perceive manufacturing, enabling the creation of complex components with unparalleled accuracy.
As we journey forward, the domain of CNC continues to be a hotbed of innovation, with emerging technologies promising to redefine the boundaries of what’s possible. The integration of AI, Industry 4.0, and sustainable practices are not just trends but are shaping the very core of CNC machining. Looking ahead, the prospects in precision machining CNC are poised to play an even more integral role in shaping the future of global manufacturing.

