
With the wave of industrial automation vigorously sweeping across manufacturing sectors, understanding how this transformation impacts different aspects of operations becomes crucial. One field experiencing tremendous change is CNC Machining, where automation is fundamentally altering the dynamics of production. This analysis navigates through the sphere of CNC Machining Automation, breaking it down from basic principles and leading up to its groundbreaking applications and challenges. It also cuts across the emerging technologies and AI-driven devices reshaping this industry, assessing their effects and how they’re converging to make CNC processes leaner and more efficient.
Key Takeaways are:
- CNC Machining Automation is a system where manufacturing processes are controlled by computer-coded commands, leading to high precision, efficiency, and economical production techniques.
- Key Technologies Driving CNC Automation include augmented reality, the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, robotics, cloud computing, and additive manufacturing.
- Benefits of Automating CNC Machining include increased operational efficiency, precise error detection, predictive maintenance, reduced downtime, and cost savings.
- Challenges and Solutions in CNC Machining Automation include initial investment costs, integration of different systems, data security, complexity of controlling automated systems, power deficiency, and environmental sustainability.
- Future Trends in CNC Machining Automation involve augmented reality, Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, robotics, and additive manufacturing, which will revolutionize the industry and enhance precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Understanding CNC Machining Automation
The rapid technological metamorphosis within the industrial world has brought forth numerous innovations, one prime example being CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Machining Automation. A revolutionizing force, this technology has become instrumental for industries seeking high precision, efficiency, and economical production techniques.
At its core, CNC Machining Automation is a system where manufacturing processes – notably cutting, milling, and drilling – are orchestrated and controlled by computer-coded commands. It’s a departure from manual control, where machine operations are maneuvered via levers and buttons. Imagine a world where a pre-programmed software oversees all machine data input and manipulation, driving exceptional manufacturing standards. Essentially, that’s what CNC Machining Automation does.
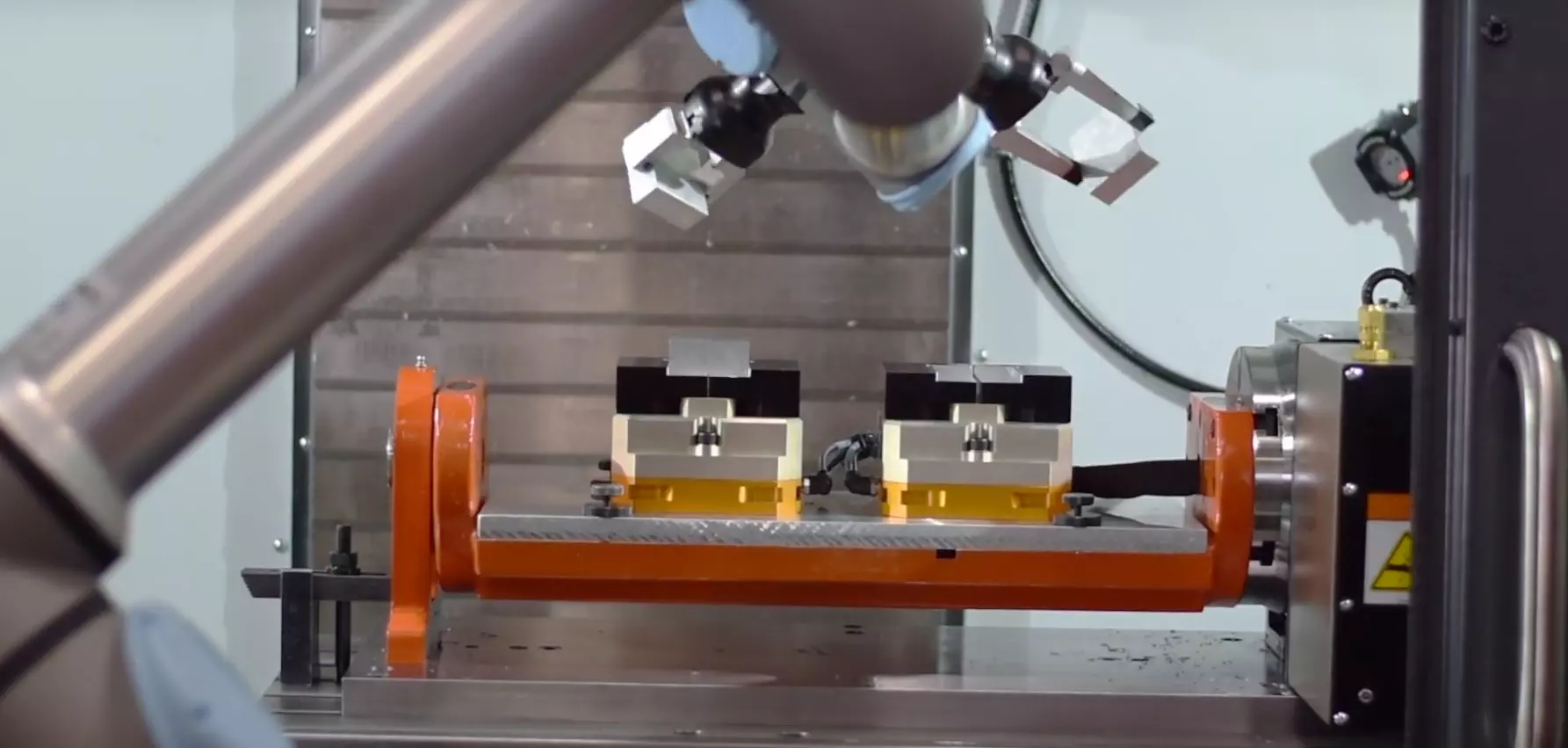
Under the hood of this intricate technology lies an ingenious blend of CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) systems. The journey begins with a CAD diagram – a 2D or 3D design of the final product. The CAM system thereafter transforms this design into CNC machine-readable G-codes, dictating the precise machine actions required for production. This sequence ensures notable accuracy in developing complex and detailed components across various industries like automotive, aerospace, medical, and more.
With CNC Machining Automation, machine errors resulting from direct human control are significantly reduced. It imparts a certain level of autonomy to machines, allowing them to run for extended periods unattended. Describe this scenario as a sophisticated symphony, where each machine plays an orchestrated part towards a product’s creation – sans conductor.
A notable highlight of this technology is its accommodations for multi-axis operations. Many advanced CNC machines offer 5-axis to 9-axis machining. This capability means one can perform multiple machining operations with a single setup, thereby reducing lead times and increasing efficiency – a revolution in the production realm.
CNC Machining Automation also encourages a safer workplace. With machines taking over hazardous tasks, there’s minimization in the risks associated with the hands-on operation of heavy machinery. This automation ensures a greater safety measure and peace of mind for industries.
Adopting CNC Machining Automation ushers in a ripple of advantages such as reduced labor costs, higher productivity, amplified speed and precision, and improved scalability. However, accompany this shift with a voracious quest for learning – as the operation and maintenance of these machines demand a new set of advanced skills. Progressing to a future where machines rule the roost may be a stretch for a few, but the potential benefits are undeniable.
In the era of technological prowess, CNC Machining Automation stands at the helm, bringing forth radical shifts in manufacturing methodologies. The profound effects of this innovation continue to ripple through industries, signaling a new age of efficiency and precision in manufacturing channels. With CNC automation, the industry limitations are swiftly dissolving, paving the way for a technologically vibrant manufacturing future.
Key Technologies Driving CNC Automation
Heading into the digital era, industries have made it a point to dig up the latest technology trends that best optimize their operations. Among these advancements, CNC Machining stands out, revolutionizing the realm of manufacturing. Current advancements include augmented reality, the Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence – all driving the wave of automation within CNC Machining.
Physical manufacturing has metamorphosed in recent years, driven largely by the incorporation of Augmented Reality (AR) into CNC Machining. AR equips machinists with real-time information about machine operations, consequently improving quality control. AR glasses, for example, offer a hands-free control while operating machinery, creating a symbiotic human-machine interface. This technology also serves at accelerating the learning curve for operators through advanced training simulations.
Peering deeper into the ocean of technological advancements, the Internet of Things (IoT) has made significant inroads into CNC Machining. The fusion of IoT-and-CNC prolongs the lifecycle of machines by predicting maintenance needs through continuous monitoring of machine health. Additionally, employing IoT feeds agility into the production line and reduces downtime, thereby facilitating smart management of manufacturing processes.
Perhaps the most pivotal game-changer in CNC Machining is the introduction of Artificial Intelligence (AI). Deep learning algorithms anticipate possible faults by analyzing operations in real-time, thus averting catastrophic failures. Further, AI has allowed for automation of inspection processes that have traditionally been time and resource-intensive. Some AI-enabled vision systems can even perform tasks like examining surface finish quality, rendering human intervention irrelevant.
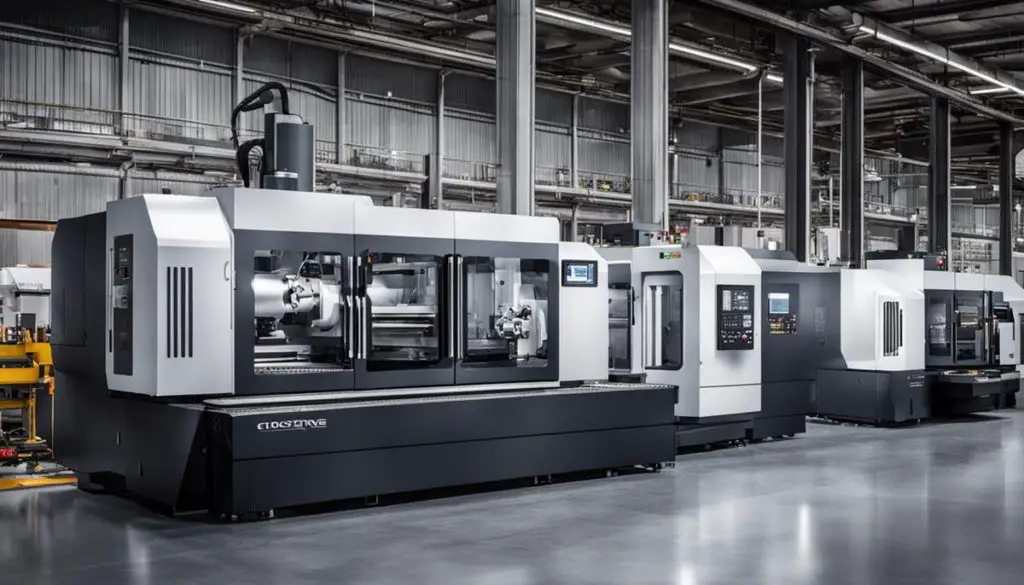

Robotics represents another significant milestone driving CNC Machining’s automation. Collaborative robots, or cobots, amplify operational productivity by performing functions like routine maintenance, machine tending, and part removal autonomously. These automating agents not only delegate mundane tasks to robots but also diminish potential human errors.
Cloud computing also takes center stage in propelling the automation revolution within CNC Machining. Cloud platforms have simplified data gathering and analysis from different machines efficiently and remotely. This unprecedented access to data harnesses improved decision-making, empowering manufacturers to swiftly respond to faults and streamline workforce deployment.
Lastly, additive manufacturing, notably 3D printing, has found great utility in modern CNC Machining. This technology involves creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file, thereby eliminating the need for molds or dies. Thus, automation in CNC machining through additive manufacturing saves time, reduces waste, and increases production speed.
Technological advancements in CNC Machining have ventured far beyond traditional boundaries, ushering in an era of automation. By embracing these paradigms, corporations can churn out higher quality products, shorten delivery time and increase revenue generation. Now, the only challenge formatting is adapting swiftly to this wave of change making sure not to fall behind in the rat race.
Benefits of Automating CNC Machining
Automation and digitization are rewriting the rulebook for CNC machining, providing a plethora of opportunities for improvement and expansion. It is rapidly transcending the limitations of traditional practices and is set to define the future of the manufacturing industry.
Diving headfirst into the era of ICT (Information and Communications Technology), CNC machining is leveraging the potential of cutting-edge technologies, such as AI, IoT, AR, Cloud computing, Robotics and Additive manufacturing. Each brings with it a unique set of benefits that significantly amplify the capabilities and reach of CNC machining.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is already revolutionizing CNC machining. Not only does AI bring in increased operational efficiency and precise error detection, it also aids in predictive maintenance, reducing downtime. Meanwhile, machine learning algorithms are being used to optimize production strategies, and deep learning to automate quality assurance processes.
When merged with CNC machining, the Internet of Things (IoT) enables machines to communicate with each other seamlessly. Machine-to-machine communication allows these systems to share real-time operational data, from temperature variations to minor malfunctions. This results in faster decision-making capabilities, proactive maintenance, reduced waste, and ultimately, cost savings.
Augmented Reality (AR) broadens the horizons of CNC machining operator training. With AR, operators can be trained using real-world simulations that help them familiarize themselves with the functioning of the machine, significantly reducing the risk factor.
Cloud computing introduces flexibility and scalability to CNC machining. Through cloud services, machines can access vast databases of operational information, allowing manufacturers to work from anywhere, at any time. Furthermore, cloud-based backup systems reduce the risk of data loss.
Robotics has had a profound impact on CNC machining, taking it a notch above manual operation. Automated robots can function round the clock, ensuring consistent output, reducing labor costs and increasing productivity.
Last but not least, Additive Manufacturing, or 3D printing, allows for the production of complex geometries that were earlier unachievable. It has given CNC machining the capability to create highly detailed and potentially customizable products, which is particularly beneficial for industries like Aerospace, Automotive and Medical devices.
Embarking on this digital journey isn’t without its challenges. For companies to reap the full benefits of this technological revolution, they need to address concerns like data privacy, security, integration of systems, costs involved in updating facilities, training staff to manage advanced machinery, and maintaining a balance between man and machine.
Endeavoring to overcome these hurdles is a small price to pay for a head start in the race towards the future of manufacturing. The technological advancements in CNC Machining are opening doors to new possibilities and transforming manufacturing into a more efficient, secure, and productive sector. The companies that are early adopters of these technologies not only stand to gain a competitive edge but are also poised to define the blueprint for the manufacturing industry of the future.
Challenges and Solutions in CNC Machining Automation
As the race towards complete automation evolves, an array of challenges has emerged in the field of CNC Machining Automation. Yet, technology continues to deftly maneuver and adapt to these challenges, consistently forging solutions that propel the industry towards its fully-automated goal.
A major challenge posed in the automation of CNC machining is the initial investment cost. The acquisition and implementation of sophisticated machines and technologies like IoT, AI, AR, and robotics come with hefty price tags. However, when the long-term benefits such as boosted productivity, reduced labor costs, and enhanced accuracy are factored in, the Return on Investment (ROI) becomes easy to comprehend and justify.
The integration of different systems and technologies also poses a complex challenge. While many manufacturing plants have older systems still in operation, intermixing them with new, advanced technologies can become an intricate task. There may be inconsistencies in data formats and communication protocols. The solution? Standardization. Industry standards need to be established and adhered to, ensuring smooth integration and interoperability between systems.
Another notable issue is the concern regarding data security, particularly with the rise of cloud computing and IoT in CNC Machining. As an influx of sensitive information traverses the interconnected web of machines and systems, the chances of cyber threats or breaches increase. To counter this, robust cybersecurity measures are becoming increasingly essential in CNC Machining Automation.
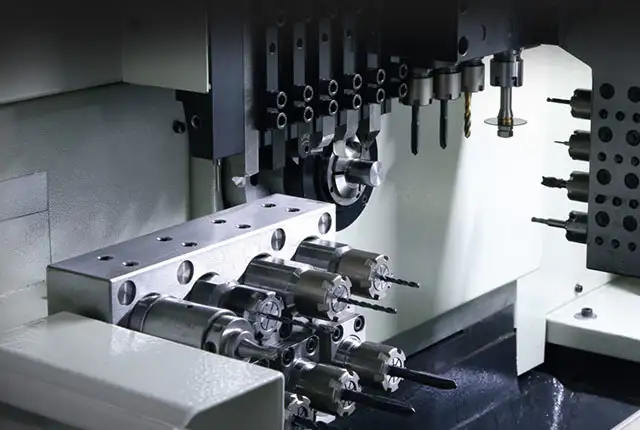

Dealing with the complexity of controlling automated systems is another challenge that the industry faces. With the incorporation of AI, IoT, and other digital advances, operating such systems can become demanding. Moreover, diagnosing malfunctions or breakdowns in such intricate systems can be a time-consuming process. This calls for an adept workforce capable of managing these advanced systems, indicating not just the need of upskilling current workers but also recruiting new talent versed in new technologies.
While discussing challenges, the role of power deficiency cannot be ignored. With the burgeoning use of automation in CNC machining, power consumption is escalating. However, renewable energy resources are being looked upon as a viable solution to mitigate these power constraints.
Similarly, maintaining the high precision and accuracy of machines during long operational hours requires regular monitoring and can trigger frequent pauses during production. Here, artificial intelligence and machine learning come into play. Predictive maintenance, an AI-enabled technology, helps in predicting machine ‘downtime’ and prompts preemptive maintenance, thereby reducing the chances of abrupt halts in production.
Last but not least, there is the ever-pressing challenge of environmental sustainability. The manufacturing industry is under global scrutiny for its environmental impact. Newer technologies are offsetting this by enabling more resource-efficient manufacturing processes. For example, Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) contributes to sustainability by reducing scrap waste and conserving raw material.
The ride to complete automation, therefore, might have its own share of bumps, but with persistent advances and problem-solving through technology, anticipate arriving at the destination more conveniently than ever.
Future Trends in CNC Machining Automation
The trajectory of technological development is steering the evolution of CNC Machining Automation towards unparalleled advancements. While there has been considerable progress in the field, the dawn of disruptive technologies heralds the future of this industry. Scanning the horizon reveals a fascinating vista of breakthroughs, where the mighty forces of AI, Internet of Things, cloud computing and more are set to shape the future of CNC Machining Automation.
Navigating the Technological Revolution in CNC Machining Automation
Augmented Reality (AR) is a key buzzword in this context. By overlaying a physical real-world environment with perceivable digital information, AR can contribute significantly to the domain, especially when it comes to training operators. This technology aims to intensify the sensory perception of the cognitive interaction with a digitally manipulative environment. Imagine operators being able to scrutinize CNC machining operations in real-time, without the physical constraints of actual machinery. This not just amplifies safety measures, but also drastically cuts down on orientation times.
Another ace up the sleeve is the Internet of Things (IoT). By enabling integration of different systems and technologies, machine-to-machine communication escalates in efficacy. IoT is the wind beneath the wings of real-time data sharing, predictive maintenance, and systemic responsiveness. What this implies is reduced downtime, significant reliability, and improved machine lifespan, underscoring IoT’s needed role in CNC Machining Automation.
Artificial Intelligence, particularly Machine Learning algorithms, possesses the potential to vastly increase efficiency in this sector. When AI and Big Data shake hands, trends get monitored, patterns are predicted, and machine self-correction becomes a practical reality. Beyond doubt, this paves the pave for a manufacturing culture defined by improved quality, lower waste, and, most importantly, reduced human intervention.
As Cloud Computing permeates sectors, its marriage with CNC Machining Automation is highly anticipated. By offering vast virtual scopes of data storage, it eliminates infrastructure costs. Moreover, with the power to secure data better, Cloud Computing nudges the manufacturing process a notch up in terms of security and economy.
The advent of robotics in this mechanized landscape further pushes the envelope. Robots can be programmed to perform tasks with high precision and accuracy, beyond what human hands are capable of, thus significantly accelerating productivity.
The transformative potential of additive manufacturing, specifically 3D printing, also deserves distinctive mention. CNC Machining stands to benefit from this trend as additive manufacturing offers prototypes quicker, accelerates cycle times, and reduces waste owing to its highly precise nature.
Revolutionizing Manufacturing: AR, IoT, and Cloud Computing in CNC Automation
However, embracing this brave new digital world poses its unique challenges. Chief among them is the sizable initial investment needed. The cost of assimilating cutting-edge technology into operations can be steep, intimidating smaller players in the sector. Other issues include managing the complexity of controlling automated systems, dealing with power deficiency, and striving for environmental sustainability.
Yet these challenges are surmountable, especially when contrasted with the promising future that CNC Machining Automation holds. As tech enthusiasts wielding technology’s power to solve problems, it’s essential to keep abreast with the fundamental trends shaping this industry. The future of CNC Machining Automation, supported by these advancements, is not just about robotic precision; it’s about the strategic deployment of tech-solutions to create a foolproof, efficient, and economical manufacturing methodology. Embracing them is not a choice, it’s an imperative. For the industry, for progress.
Facing forward, CNC Machining Automation is paving the way for revolutionizing manufacturing and production. With emerging technologies like AR/VR and 3D printing poised to disrupt this sector further, the contours of CNC automation are likely to be redrawn in exciting, unprecedented ways. Coupled with tailored solutions to tackle existing obstacles, the future predicts a thriving landscape where precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness are heightened. As such, embracing these transformations is pivotal in riding the tide and harnessing the full potential that CNC automation promises to catapult production realms into a new era of digital manufacturing.

