In the ever-evolving world of technology, two particular innovations, the Internet of Things (IoT) and Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining, are making significant strides. These powerful technological developments, when combined, pave the way for a new level of efficiency and accuracy in machining operations. With the seamless amalgamation of IoT and CNC machining, the industry is witnessing an unprecedented transformation, enhancing productivity and quality outcomes. The intersection of IoT and CNC machining spawns a myriad of possibilities, ultimately seeking to streamline operations, minimize resource wastage, and maximize overall performance.
Key Takeaways are:
- The Impact of IoT on CNC Machining: The combination of IoT and CNC machining is revolutionizing the industry, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in machining operations.
- Understanding IoT and CNC Machining: IoT is a network of devices that exchange data over the internet, while CNC machining is a high-precision manufacturing process.
- The Intersection of IoT and CNC Machining: IoT technology is integrated into CNC machines, allowing for real-time data sharing and data-driven decision-making processes.
- The Real-Life Impact: IoT-enabled CNC machines can predict maintenance needs, automate the supply chain, optimize manufacturing processes, and improve product quality.
- How IoT is Incorporating into CNC Machines: IoT implementation in CNC machines involves embedding sensors, using an IoT platform for data processing, and employing communication protocols and data visualization tools.
- The Benefits of IoT in CNC Machining: IoT improves smart monitoring and proactive maintenance, quality control and assurance, energy efficiency, workforce enablement, and interoperability.
- Real-life Examples of IoT in CNC Machining: IoT is used for smart monitoring, quality control, energy efficiency, workforce enablement, and interoperability in CNC machining.
- Challenges and Solutions in Implementing IoT in CNC Machining: Challenges include data integrity and privacy concerns, managing complex data sets, ensuring interoperability, overcoming workforce and knowledge gaps, and managing cost constraints.
- Strategic Approach to IoT-CNC Integration: Addressing challenges strategically and adopting a thoughtful approach can lead to successful IoT-CNC integration.
- Navigating Solutions for IoT-CNC Integration: Solutions include careful planning, prioritizing security, gradual integration, and leveraging financial support.
Understanding IoT and CNC Machining
The Intricate Relationship Between IoT and CNC Machining Unveiled

As the world of technology continues to evolve at breakneck speed, two terms consistently hold the limelight: Internet of Things (IoT) and Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining. While it is easy to see these two concepts as separate entities functioning in different facets of technology, they are fundamentally interconnected, working in tandem to yield marvels in modern tech-driven operations—the sort of advancements that would make any tech enthusiast’s heart rate quicken with excitement!
The Internet of Things, widely known as IoT, is a network of devices, vehicles, and appliances embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to connect and exchange vital data over the Internet. Think of it as a grand orchestration of ‘smart‘ objects, communicating among themselves and the cloud, driving automation, and enhancing overall efficiency in numerous industries.
The Intersection of IoT and CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, on the other hand, is a manufacturing process known for its high precision and efficacy. CNC machines are programmed to perform complex cuts in large volumes, rendering them instrumental in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and healthcare.
On the surface, the bond between IoT and CNC may appear ambiguous. However, considering the intrinsic motivation driving both of these technologies – automation and efficiency – it is no surprise that their paths converge.
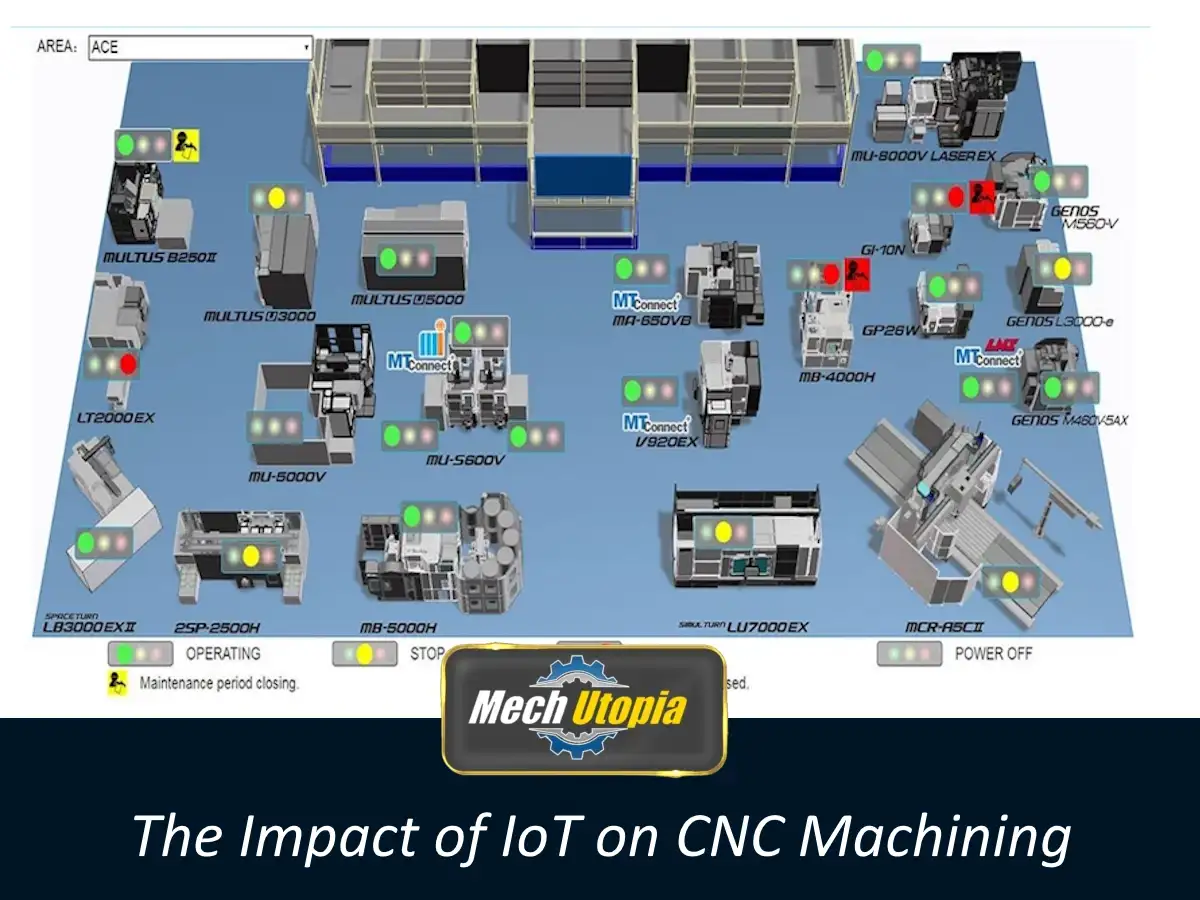
CNC machines, equipped with smart technology and embedded sensors, harness the power of IoT by sharing real-time data about machine performance, work schedules, tooling condition, material status, and much more. This stream of information is processed in the cloud, allowing for robust data-driven decision-making processes.
The Real-Life Impact
An example of this synergy in real-world applications is predictive maintenance. Utilizing IoT technology, CNC machines can now track and analyze performance data to predict potential mechanical failures. This allows operators to address mechanical issues before they result in costly equipment downtime, significantly enhancing productivity and cost-efficiency.
Similarly, IoT-fueled CNC machines can automate the supply chain as per real-time demand and supply fluctuations, reducing material waste and operational downtime. The monitored data can be used to optimize the manufacturing process, improve product quality, and speed up production times, providing a significant competitive advantage.

Where Do We Go From Here?
The intersection of IoT and CNC machining is not just a fleeting trend amongst tech aficionados, it’s a revolutionary step in automation that will shape the industrial landscape in the coming years. As we move forward, expect deeper integration between these two phenomena, unlocking new opportunities for innovation and efficiency. However, as with any tech advancement, challenges such as data security, interoperability, and seamless integration are hurdles that have to be jumped. As technology continues to evolve, there’s no doubt these challenges will be met with ingenious solutions, leading to an ever more connected, automated, and efficient technological future.
How IoT is Incorporating into CNC Machines
Rolling out IoT for CNC machines commences with embedding sensors and actuators on the machine parts. These sensors collect various data points during the machining process – temperature, vibration, speed, and force exerted, to name a few. The data amassed is then transmitted to a central system for real-time processing and analysis.
The critical element steering this implementation process is an IoT platform, which serves as a bridge relaying machine data to a user interface. Here, various tech giants offer an array of IoT platforms, each with its unique set of features and functionalities.
However, the following key advantages encourage choosing a cloud-based IoT platform. Firstly, it allows for seamless data sharing between different systems. Secondly, it ensures high availability and scalability, crucial for managing, storing, and processing large data volumes. Lastly, it reduces upfront installation costs and ongoing IT maintenance requirements.
Once the IoT platform is decided, a robust communication protocol is necessary. It’s the foundation for facilitating a secure and reliable data transfer from CNC machinery to the IoT platform. Among the various choices available, MQTT and TCP/IP are widely used due to their low power consumption and high data transfer efficiency.

Visualizing and analyzing data is another pivotal step in the process. Data visualization tools like SCADA systems, OPC servers, and dashboards are employed to monitor machine data in real-time. For data analysis, predictive algorithms and machine learning tools identify patterns and highlight anomalies, paving the way for predictive maintenance and improved operational efficiency.
Furthermore, one cannot overlook the importance of digital twins in this implementation phase. Creating a digital representation of the CNC machine enables real-time tracking, testing, and optimization, minimizing downtime and maximizing production output.
Securing the IoT ecosystem is also paramount. Employing standards such as SHA-256 for data encryption or using hardware security modules (HSMs) to manage and protect digital keys are advocated. Regular security audits are indispensable to uncover any potential chinks in the armor.
The final step in this implementation journey is the continuous evaluation and optimization of the IoT-CNC integration. Refined models and advanced algorithms enhance predictability and precision, while staying abreast of the latest industry trends and standards can mitigate any unforeseen threats or challenges.
Despite the complexity, implementing IoT in CNC machinery is a pursuit worth taking. Not only does it herald a new era in machine tool technology, but it also expands the horizon of manufacturing possibilities. By intelligently merging machines and data, it blurs the line between the physical and digital manufacturing world – a profound step toward a truly connected Industry 4.0.
The Benefits of IoT in CNC Machining
As we delve deeper into the tight-knit relationship between the Internet of Things (IoT) and CNC machining, several improvement areas come to light that are spearheading changes to the traditional CNC machining processes. Let’s zoom into the fascinating ways that IoT is transforming the landscape of CNC operations, beyond the points already covered.
Smart Monitoring and Proactive Maintenance:
If you thought data collection and analysis were the core improvements IoT delivers, hold onto your seats because smart monitoring is another game-changer. Real-time machine monitoring systems are powered by IoT-enabled sensors that provide rich and immediate insights into CNC machinery’s working conditions. This allows operators to spot malfunctions and worn components early enough to prevent costly downtimes. Predictive maintenance is enabled as a result, replacing the traditional reactive approach with a proactive one. Now, that’s efficiency delivered!
Quality Control and Assurance:
IoT streamlines quality assurance processes in CNC machining by leveraging machine learning models to ensure products meet exact specifications. This significantly reduces the frequency of defective parts, and in the long run, increases productivity. Precise sensors and advanced analytics work in synergy to flag or reject non-conforming parts, saving costs associated with rework or waste.
Energy Efficiency:
Another edge IoT brings to CNC operations lies with energy consumption. Sensors integrated into CNC machines provide vital data on energy usage, enabling the system to identify and address inefficiencies. This leads to significant energy savings, cost reductions, and even a greener footprint – a win at multiple levels.
Workforce Enablement:
Despite the levels of automation, human interaction still plays a crucial role in CNC machining. IoT comes to the forefront here by providing workers with tools for remote machine monitoring and control. With a well-structured IoT system, operators can oversee and manage operations from practically anywhere, leading to flexibility, reduced response times, and enhanced productivity.
Interoperability & Interconnectivity:
With IoT, CNC machines can communicate seamlessly with other devices within the ecosystem. Whether it’s a collaborative robot (Cobot) or an automatic guided vehicle (AGV), the possibilities of interoperability are indeed vast. This connectivity transforms standalone machines into a collaborative, automated network, accelerating various processes and enabling comprehensive control over the entire production process.
To optimize CNC machining operations, IoT’s power shouldn’t be underestimated. As advancements continue, expect to see an even deeper fusion between these two technological giants, leading to fresh approaches to traditional CNC machining problems. After all, the intersection of smart technology and industry is where the magic happens as we stride forward to realize Industry 4.0 ambitions.
Real-life Examples of IoT in CNC Machining
Practical Examples of IoT Usage in CNC Machining
Smart Monitoring and Proactive Maintenance
One of the most utilized benefits of IoT within CNC machining lies in smart monitoring and proactive maintenance. Sensors integrated into CNC machines monitor vital operational parameters like temperature, vibration, force and power. This real-time data, fed into an IoT platform, provides insights into the machine’s health and allows for pre-emptive maintenance, significantly reducing instances of unexpected downtime.
Quality Control and Assurance
Quality control has always been a priority for manufacturers, and with the convergence of IoT and CNC machining, quality assurance is more efficient than ever before. By employing sensors and precise data analytics, discrepancies during the manufacturing process are identified and corrected in real-time. Essentially, variations are detected early, hence preventing the production of flawed parts.
Energy Efficiency
IoT applications in CNC machines also contribute to energy efficiency in manufacturing industries. Here, intelligent sensors are particularly useful in monitoring energy consumption, and detecting abnormalities or areas of inefficiency. With consequent adjustments, companies can reduce energy consumption, maintain performance levels, and witness cost savings.
Workforce Enablement
IoT isn’t just about machine automation; it also empowers the human workforce. With IoT, operators and managers can remotely track, monitor, and analyze the performance of their CNC machines. This offers unprecedented visibility, enabling smarter and faster decisions, creating a more productive and efficient work environment.
Interoperability & Interconnectivity
In modern manufacturing settings, different machines need to communicate seamlessly and the pairing of IoT and CNC machining paves the way for this interoperability and interconnectivity. Sensor-equipped CNC machines can share their status, performance and issue alerts with other devices on the factory floor in a streamlined manner. This creates a connected factory environment, optimizing production, streamlining the supply chain, and creating opportunities for automation.
Undoubtedly, IoT is transforming the realm of CNC machining, paving the way for unprecedented efficiencies, minimizing waste, and creating a robust manufacturing landscape. By embracing this evolving technology, companies can stay at the forefront of innovation, maintaining competitiveness in today’s fast-paced market.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing IoT in CNC Machining
Now, it’s time to delve deeper into the distinct challenges posed during the implementation of the Internet of Things (IoT) in Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining and, of course, how to navigate these hurdles.
Addressing Data Integrity and Privacy Concerns
Firstly, let’s tackle the notorious issue of data integrity and privacy. With an influx of interconnected devices, the risk of cyber threats increases proportionally. Therefore, securing IoT devices and infrastructure becomes a paramount concern. Implementing robust security protocols, firewalls, and encryption algorithms is the solution, combined with regular audits of the system to ensure that all defenses are up to date and functional.
Managing Vast and Complex Data Sets
The data itself, gathered from tooling machines, is vast and complex in nature. Managing this colossal amount of data can be daunting. IoT integration involves the conversion of these data sets into meaningful insights driving value-added actions. Thus, data management software, coupled with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to handle and analyze big data, should be tailored into the system design.
Ensuring Interoperability of Devices and Systems
Another potential roadblock is the interoperability of devices and systems. The seamless communication between different IoT devices and networks is critical. To address this, it’s essential to establish a standardized system of communication protocols. Manufacturers and industry bodies must work together to adopt universal standards, thereby ensuring compatibility between various IoT devices and their subsequent integration into the existing infrastructure.
Overcoming Workforce and Knowledge Gaps
Furthermore, in the early stages of integration, there exists a lack of skilled workforce and knowledge about IoT operation and maintenance. Upskilling existing employees or hiring new talent with the necessary technical skills and competencies is significant to establish the IoT-CNC synergy effectively.
Managing Cost Constraints for IoT Integration
Last but not least, cost constraints often overshadow the potential benefits of IoT-CNC integration. Investing in IoT infrastructure requires substantial capital upfront. Persuading key stakeholders to appreciate the long-term value creation and efficiency offered by IoT can mitigate this challenge. Additionally, Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) and government subsidies can also provide financial support to small and medium manufacturing units grappling with investment-related challenges.
Strategic Approach to IoT-CNC Integration
Implementing IoT in CNC machining may pose some challenges, but the key is to address these issues strategically. This tech journey is not without hurdles, but it’s one the manufacturing domain must embark on for future growth and competitiveness. Fasten your seat belts, because the manufacturing industry is about to speed into the future with IoT-powered CNC machining.
Conclusions
While the challenges associated with implementing IoT in CNC machining cannot be overlooked, solutions abound which can mitigate these obstacles. Compatibility issues, cybersecurity threats, and high implementation costs indeed pose complexities, but a thoughtful approach incorporating careful planning, prioritizing security, and gradual integration can navigate through these challenges effectively. The world of CNC machining is set for a revolutionary upgrade, powered by IoT, and the benefits evidently outweigh the challenges. Manufacturing industries are on the brink of a new era characterized by automation, heightened productivity, reduced downtime and cost-effectiveness, all contributing towards a promising future.

