In our increasingly digital world, the role of Big Data and analytics is becoming a vital thread in the fabric of diverse sectors, notably Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining. CNC machining, though a technical aspect of manufacturing, is touching new heights of efficiency with the powerful assistance of Big Data and analytics. This fascinating intersection of cutting-edge technology and traditional industry can significantly enhance manufacturing processes, drive informed decision-making, and optimize performance. This text explores in detail, the concept, trends, applications, and potential future of Big Data and analytics in CNC machining, highlighting how these advancements are shaping the manufacturing landscape and paving the way for a bright future.
Key Takeaways are:
- Big Data and analytics are revolutionizing CNC machining
- Big Data enables zero-defect outcomes, improved productivity, and optimized production processes
- Machine analytics enhances CNC efficiency through predictive maintenance and real-time streamlining
- Analytics in CNC machining empower decision-making through simulation technologies, deep learning, and IoT
- The future of Big Data and analytics in CNC machining lies in AI, IoT, 3D printing, and blockchain
Big Data and its Role in CNC Machining
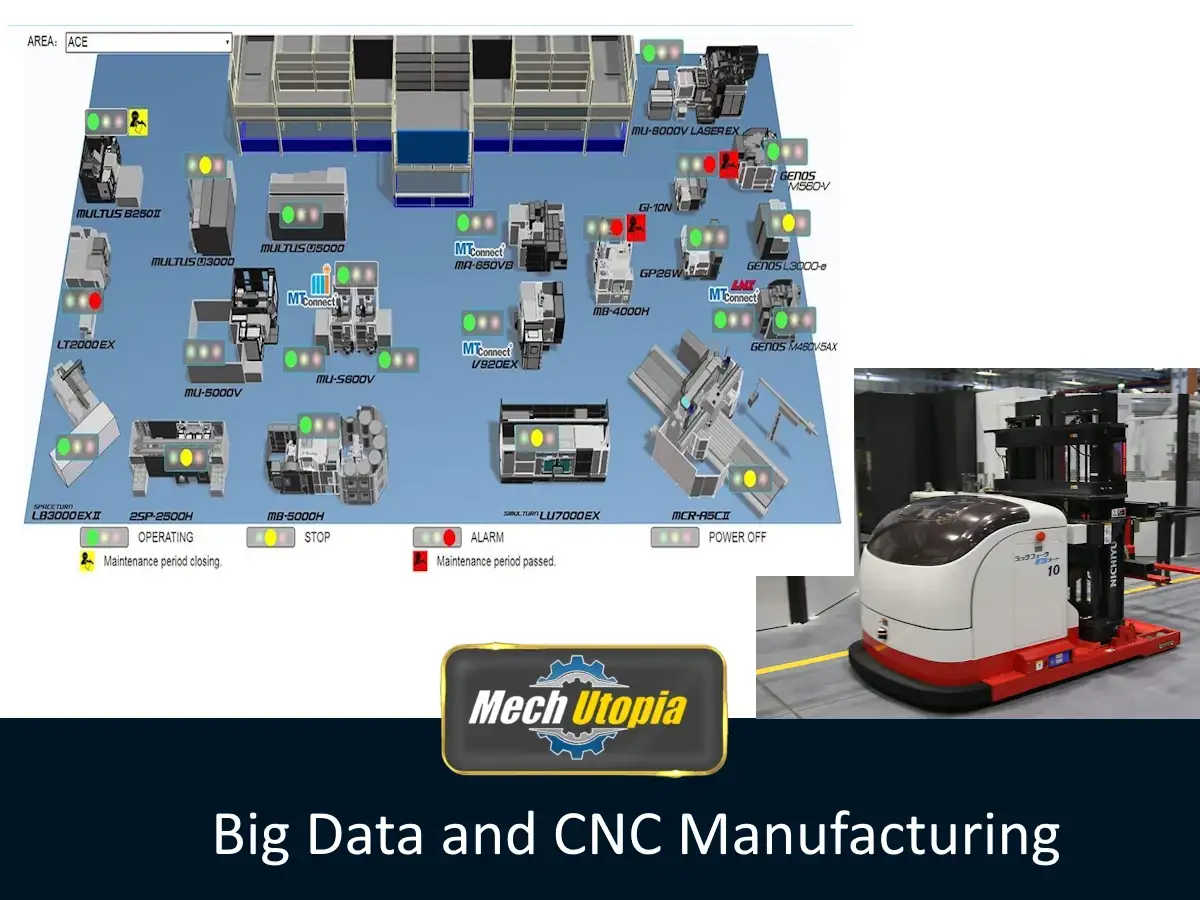
Journey with us as we delve into the technological revolution reshaping the landscape of Computer Numeric Control (CNC) machining – Big Data. With its ability to capture, process and analyze massive volumes of data in real-time, Big Data has become a game-changer in this industry. Let’s decode how.
Quality control is mission-critical in CNC machining. With the integration of sensors capable of tracking every nuance of a machine-operative process, and by leveraging the power of Big Data analytics, the industry now delivers an impressive zero-defect outcome. The paradigm of “detect and fix defects” is old news. The current narrative focuses on preventing defects altogether.
Zero defects aren’t the only perk offered by Big Data. Let’s talk about improved productivity. Massive data harvesting facilitates real-time analysis of a machine’s performance, pointing out any inefficiencies that need to be addressed. This is a major upgrade from the pre-big data scenario where technicians could only react to existing problems. Big Data enables predictive maintenance, resulting in minimized downtime, increased efficiency, and, ultimately, higher productivity.

Moreover, optimizing production processes is another huge area where Big Data is making waves. Parameters such as cutting speed or feed rate greatly influence the overall result in CNC machining. Traditionally, the optimization of these parameters could take a colossal amount of time and the immense amount of previously unused data was virtually wasted. Now, thanks to Big Data, data derived from these parameters can be analyzed promptly to fine-tune the production process, paving the way for faster throughput times.
The energy efficiency speaking point cannot be left out when discussing Big Data’s contributions. With the worldwide emphasis on energy conservation, Big Data is worth its weight in platinum. With the analysis of energy consumption data for various machining processes, strategies can be developed to optimize the use of energy. The transition from data to insight to action is game-changing, consequently leading to greener and cost-effective manufacturing processes.
From ensuring zero-defect outcome, driving up productivity, optimizing production process, to promoting energy efficiency – Big Data has indeed become the linchpin in driving CNC machining to a whole new level. Embracing Big Data isn’t just about keeping up with the times—it’s about revolutionizing the way the CNC industry operatates and taking full advantage of the technological advancements at our disposal.
Applications of Machine Analytics in Improving CNC Efficiency
The CNC machining field continues to be reshaped relentlessly. Behind this drive for continuous improvement lies an invisible yet powerful enabler: machine analytics. Building on previous strides in big data and quality control optimization, a new frontier opens up to yield substantive dividends in the realm of CNC machining.
Emerging as a transformative tool, machine analytics leverages and extends the capabilities of big data. Pivotal to this evolution is fine-tuning existing technologies and practices in CNC machining, while unlocking opportunities for smart machinery adaptation. Essentially, machine analytics is ushering in a new era of efficiency, where every scrap of data can be harnessed to optimize operations.
Harnessing Machine Analytics for Unrivaled CNC Efficiency
In the race for productivity and quality outcomes, preventative and predictive maintenance driven by machine analytics is becoming a reality. This approach relies on sophisticated algorithms and in-depth data analysis to anticipate machine failures before they impinge on the production process. No more downtime; every second is harnessed for optimum productivity. Reduced machine maintenance costs are icing on the cake.
But machine analytics isn’t confined to predictive maintenance. Interwoven into this data-driven strategy is the objective of streamlining operational processes. This real-time streamlining necessitates having a pulse on the flow and status of operations – an area ripe for machine analytics.
CNC machines, laden with sensors, are now transformed into data-generators. Information regarding processes, operations, and performance is continually captured, analyzed, and leveraged to fine-tune processes. Machinery’s health status, performance indicators, operational bottlenecks – all become visible, actionable insights. Thus, machine analytics along with real-time data translates into precise micro-adjustments that refine operations and maximize efficiency.
Energy consumption has always been an area of concern for CNC operations. The rise of machine analytics exhibits remarkable prospects for reducing this drain. Analytical software that intuitively learns from machine behavior can calibrate machine performance, optimizing performance while minimizing energy expenses. Machine analytics, therefore, promises a sustainable production line that synergizes efficiency and conservation.
Embracing machine analytics goes beyond aligning with an industry trend; it signifies the recognition of data as a critical operational currency. The comprehensive impact of this powerful tool delves deeper than surface level improvements, digging into the gold mine of operational data to propel CNC machining to new efficiency heights. CNC machining shops that fully harness this powerful tool will be poised to lead the pack in performance, quality, and efficiency.
Although the advent of machine analytics in CNC machining is still in its early stages, early adopters are already experiencing substantial performance improvements. It is beyond doubt that the integration of machine analytics will continually drive up efficiency and push the capacity boundaries of CNC machines while minimizing wastages and reducing operational costs.
The forward march of technology in CNC machining is undeniable and unstoppable. Bearing witness to its potential, machine analytics is undoubtedly an essential tool for those desiring to remain at the cutting edge of the industry.
The Decision-Making Power of Analytics in CNC
When speaking about CNC machining, the conversation quickly shifts to powerful advancements brought about by an intersection of Big Data and Machine Analytics. The integration of these two juggernauts of technology had unleashed a new era in the manufacturing landscape, propelling decision-making capabilities to entirely new frontiers.
Simulation technologies, for instance, are making noise in CNC machining. Often coupled with machine analytics, actionable insights derived from these simulations empower manufacturers to make informed predictions and eliminate costly trial-and-error tactics. Such a tech-enablement can, predictably, spot engineering distortions before they become a real problem, thus preventing costly blunders.
Deep Learning, an off-shoot of Machine Learning (ML), is also seeping into CNC machining. Deep Learning algorithms can examine a huge amount of data sets – or Big Data – and learn from it, enhancing the decision-making process gradually. This involves spotting inefficiencies and discrepancies in machining processes, and hence identifying opportunities where improvements can be implemented.
Moreover, there’s a profound uplift in predictive maintenance offshoots, primarily led by the proliferation of IoT (Internet of Things) in CNC machining. Wireless sensors placed on CNC machines give real-time updates about the machine’s performance and any possible errors. Such in-depth visibility, often relayed to control rooms via integrated platforms, imbues technicians with remarkable preemptive abilities to tackle glitches before they occur. This improves machine lifetime, saves costs, and promotes uninterrupted workflow.

The amalgamation of Digital Twin technology and machine analytics is another landmark advancement. This involves creating an exact digital replica of the physical CNC machine. Thanks to embedded IoT sensor networks, data is consistently fed into the digital twin, which serves as a testing ground for trial runs. The result? Vastly improved forecasting and decision-making, negating need for physical prototypes and saving considerable resources.
Collaborative robots, or ‘cobots’ in the industry parlance, influence CNC machining decision-making as well. Typically equipped with Machine Vision enabled by AI, cobots interact seamlessly with human technicians and other machines. They ensure greater precision, efficiency, and safety in CNC machined operations.
Lastly, advancements in cloud computing can’t be ignored. Manufacturers who leverage the cloud tech can store, process, and access vast amounts of data quickly and at a lower cost. This significantly enhances decision-making capabilities, resulting in a leaner, more efficient, and more cost-effective operation.
Accelerating at an unprecedented pace, the inclusion of big data, machine analytics, and other technological enhancements within CNC machining depicts an exciting future. With analytical capacity intensifying and decision-making capabilities bolstering, the industry is propelling into a new era of efficiency and productivity. The impact is undeniable – the tech-savvy would do well to keep their eyes trained on the horizon for the next leap forward in this relentless technological march.
The Future of Big Data and Analytics in CNC Machining
When peering into the crystal ball for the future of Big Data and analytics in CNC machining, one cannot help but keep the gaze firm on two buzzwords: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies aren’t simply the next step in the industrial revolution, they are set to massively disrupt the way CNC machines operate, interact and evolve.
AI’s key role in future CNC machining pertains to automation and decision-making. Think of AI as an autonomous system capable of making independent decisions, whether it’s about workflow optimization, troubleshooting, or preventive maintenance based on the Big Data it’s fed. This includes everything from monitoring tiny deviations from production norms to identifying signs of wear and tear often invisible to the human eye. By preemptively identifying these issues, downtimes can be reduced dramatically.
The potential of machine learning, a subset of AI, is also immense. With every byte of data, the system learns, adapts, and optimizes itself. This constant refinement of processes and actions makes the machine more efficient and less prone to errors over time. Imagine self-learning CNC machinery that evolves its operation protocols based on the data it receives, resulting in near-perfect production outcomes.
IoT, on the other hand, brings about limitless possibilities in interconnectivity. CNC machines will no longer be standalone entities but integrated parts of a cohesive manufacturing network. With IoT, each machine can share data, synchronize operations and collaborate by learning from other units’ experiences. This provides a holistic overview of the operations, enabling us to pinpoint bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or issues faster than ever before.

A significant future prospect also lies in the integration of 3D printing with CNC machining. Such a combination can provide unprecedented flexibility and precision, transforming manufacturing as we know it. This amalgamation benefits from big data analytics in selecting materials, tool paths and providing quality control for complex multi-dimensional constructs.
Blockchain, though primarily associated with cryptocurrencies, promises immense potential in data management for CNC machining. It ensures data integrity, security, and traceability, vital for quality control, compliance, and intellectual property protection. A decentralized system also boosts resilience, safeguarding against data loss or corruption.
These technologies are not a distant future but an emerging reality. Early adopters advantageously leverage these for superior operational efficiency, quality, and profitability. But as with every technological disruption, challenges such as cost, integration complexities and skilled manpower will have to be tackled.
Conclusion
The future of Big Data and analytics in CNC machining is highly promising, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. It represents an industry ripe for innovation, where the fusion of traditional machining with cutting-edge technology uplifts manufacturing processes to previously unimaginable levels. The gears are clearly in motion, and CNC machining’s tech evolution is unstoppable.
Moving forward, the continuing evolution of CNC machining will hinge upon how effectively Big Data and analytics are harnessed. The potential of AI and machine learning holds great promise, clearing the path for a new era of automated data analysis that can further revolutionize CNC machining. This rapidly expanding field will continue to provide new opportunities to optimize operational efficiency, make informed decisions and drive high-quality production. Adapting to these evolving technologies is not just an option, but a necessity for businesses seeking to stay competitive. The transformative power of Big Data and analytics in CNC machining not only signifies the dawn of a new chapter in manufacturing but also underpins its bright future in the world of Industry 4.0.

